China and Free Trade: New Agreements and Partnerships

The Chinese government considers Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) as a new platform for further opening up to the outside world and accelerating domestic reforms, and an effective approach for integrating into the global economy and promoting economic cooperation with other economies. Current Status of China’s Free Trade Agreements Currently, China has 24 free trade agreements under construction, of which 16 agreements have been signed and implemented. Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership, signed by 15 countries in Asia-Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, New Zealand, Australia, and the ten member states of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) – is the world’s largest free trade agreement. Key Free Trade Partnerships: Economic Benefits: Challenges and Considerations: Despite the benefits, China’s free trade agreements face challenges: Future Outlook: China continues to expand its free trade agreement network, with particular focus on:
China as a Destination for High-Tech Investment

China as a Driving Force for the Global Economy: Future Outlook

Earlier this year, China announced an ambitious goal to achieve 5% economic growth in 2024. Today, nearly seven months into the year, economists and government officials say they are optimistic that China can achieve its target. New Ways of Growth After the government’s open and reformist economic policies in the seventies and eighties, China’s economic growth rate was unmatched. Economic output per person, for example, increased by about 3000% in recent decades. China’s economic growth has slowed in recent years. Growth is expected to decline to 3.3% by 2029, according to the International Monetary Fund. Experts confirm that new ways of growth will be required for China to maintain steady growth. This includes expansion into new and transforming industries like artificial intelligence, digital financial services, and green technologies such as electric vehicles. High-Quality Growth In 2017, Chinese President Xi Jinping said China would transition its economy from a period of high-speed growth to a stage of high-quality growth. Today, experts confirm that focusing on high-quality growth remains vital to ensure medium and long-term economic growth. Geopolitical Headwinds Analysts point out that despite China’s positive economic outlook for 2024, obstacles and barriers to growth remain. Specifically, this includes geopolitical tensions and global economic fragmentation. The International Monetary Fund estimated last year that economic fragmentation and increased international trade restrictions could cost the global economy $7.4 trillion and cut global economic output by up to 7%.
China Invests in Renewable Energy Despite Declining Global Demand for Traditional Energy
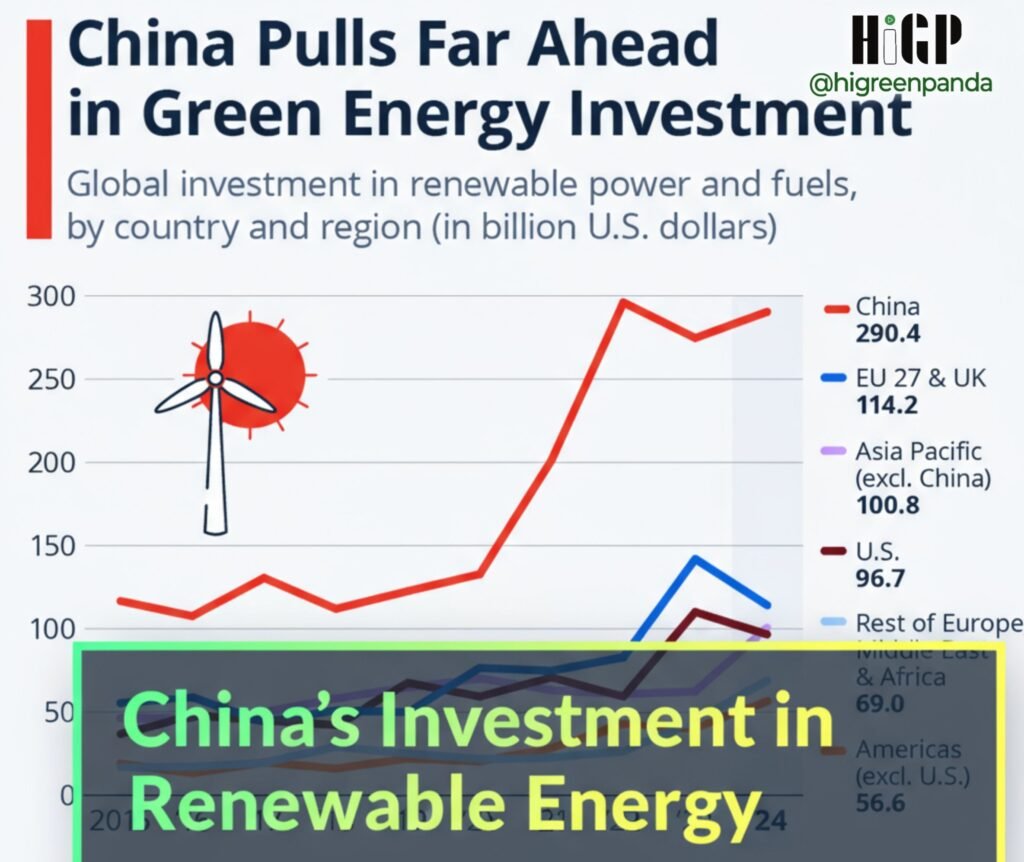
Amid increasing global challenges and declining demand for traditional energy, China continues to boost its investments in renewable energy as part of its ambitious strategy towards a sustainable future. Massive Investments in Renewable EnergyThe Chinese government has announced plans to invest over $300 billion in renewable energy projects over the next five years. These projects include the development of solar and wind power plants, as well as strengthening the infrastructure for smart energy grids. This investment aims to increase the share of renewable energy in the national energy mix to over 50% by 2030. Declining Demand for Traditional EnergyDespite the continuous growth in the renewable energy sector, global demand for traditional energy, such as oil and gas, is witnessing a significant decline. Reports indicate that many countries have begun to reduce their consumption of fossil fuels as part of their efforts to combat climate change. This global trend reflects changes in consumption patterns, as countries move towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources. Innovation in Green TechnologiesChina is considered one of the leaders in the development of green technologies, investing heavily in research and development. Chinese companies are striving to improve the efficiency of solar panels and wind turbine technology, contributing to lower production costs and increased competitiveness in global markets. The government also encourages innovation by offering financial incentives to companies that adopt renewable energy solutions. Challenges to the Transition to Renewable EnergyDespite significant progress, China faces several challenges in its journey towards a complete transition to renewable energy. Among these challenges are the necessity to upgrade electricity grids to accommodate increasing renewable energy, as well as the need for energy storage to ensure supply stability. Furthermore, reliance on raw materials required for manufacturing renewable energy technologies, such as lithium and cobalt, may pose new challenges in the supply chain. China’s Role in the Global Energy MarketChina seeks to reshape the global energy landscape by strengthening its role as a leading power in renewable energy. With increasing international pressure to reduce carbon emissions, eyes are turning to China to provide innovative and sustainable solutions. Experts believe that China’s success in this field could significantly influence the energy strategies of other countries, contributing to the achievement of global goals for combating climate change. Under these circumstances, it appears that China is moving forward with its transition to renewable energy, reflecting its commitment to sustainable development and addressing environmental challenges.
China 2025: Strategic Analysis of Fast-Growing Retail Markets for Foreign Importers

China’s imports in the first seven months of 2025 reveal shifts in demand across consumer goods and high-tech inputs, providing insights for global exporters about emerging opportunities. Overall Import Performance China’s goods imports reached 10.39 trillion yuan ($1.45 trillion), with a year-on-year decline of 1.6%. Despite negative headline growth, underlying demand showed resilience supported by policies targeting industrial upgrading and domestic consumption. Imports by Major Trading Partners Top Product Categories Implications for Global Business Three key strategic implications:
Robots and Artificial Intelligence: How China Leads the Smart Manufacturing Revolution
China has created more than 30,000 basic-level smart factories as part of its national campaign to accelerate industrial digitization and smart manufacturing. Progress in Smart Factories China has also developed: These 230 super-level factories, distributed across all 31 regional areas and covering more than 80% of national manufacturing sectors, have implemented approximately 2,000 advanced smart manufacturing scenarios. Achieved Results Performance data from these super-level facilities showed the benefits of smart manufacturing: Four Levels of Smart Factories Future Goals The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology aims to expand promotion of super-level smart factories while preparing to introduce leading-level cultivation, enhancing China’s commitment to developing smart production capabilities and global competitiveness.
The Belt and Road Initiative: A Key Pillar for a Global Community with a Shared Future
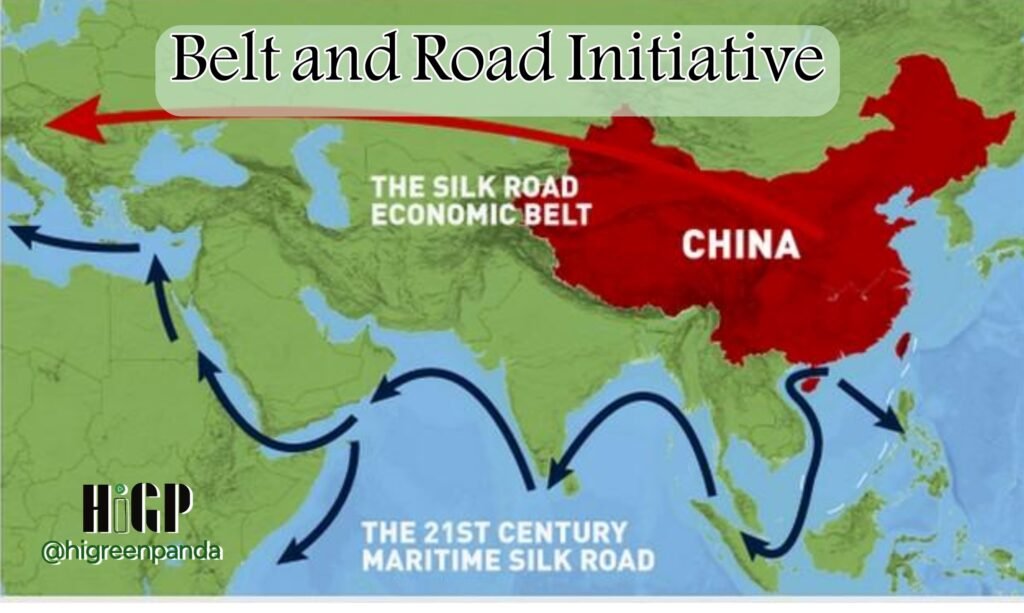
IntroductionMore than two millennia ago, our ancestors, driven by a sincere desire for friendship, traversed plains and deserts to establish the overland Silk Road, which connected Asia, Europe, and Africa, leading the world into an era of extensive cultural exchanges. Over 1000 years later, our ancestors sailed and navigated through waves to open the maritime Silk Road, connecting East and West, initiating a new phase of closer communication between peoples. The ancient Silk Roads, spanning thousands of miles and years, were not merely trade routes but also avenues for cultural exchange, significantly contributing to human progress. In March 2013, President Xi Jinping proposed the vision of a global community with a shared future; and in September and October of the same year, he put forward initiatives to join others in building the Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road (the Belt and Road Initiative, or BRI). The Belt and Road Initiative is a creative evolution that embraces and carries the spirit of the ancient Silk Roads – two of the greatest achievements in human history and civilization. It enriches the ancient spirit with the spirit of the times and the culture of the new era, providing a platform for building a global community with a shared future. Since its launch 10 years ago, and thanks to the joint efforts of all parties, cooperation under the Belt and Road Initiative has expanded beyond China’s borders to become an international endeavor. It has evolved from ideas to actions, from vision to reality, and from a general framework to tangible projects. It has been welcomed by the international community as a public good and a platform for cooperation, achieving concrete results. Over the past decade, cooperation under the Belt and Road Initiative has brought real gains to participating countries. It has contributed to the sound development of economic globalization, helped address global development challenges, and improved the global governance system. It has also opened a new path for all humanity to achieve modernization, ensuring that efforts to build a global community with a shared future yield real results. Belt and Road Initiative: A Chinese Proposal, but Belonging to the Whole WorldToday, the world is undergoing profound changes on a scale unseen in a century. Problems and challenges continue to threaten the progress of human civilization. In response to the changing global situation and the expectations of the international community, and considering the future and interests of all humanity, China proposed the Belt and Road Initiative. The BRI adheres to the spirit of the Silk Road, a great legacy of human civilization, connecting the past, present, and future. China launched this initiative, but it belongs to the world and benefits all humanity. For thousands of years, the ancient Silk Roads served as major arteries for interaction, extending across the valleys of the Nile, Tigris, Euphrates, Indus, Ganges, Yellow River, and Yangtze River. They connected the birthplaces of Egyptian, Babylonian, Indian, and Chinese civilizations, the lands of believers in Buddhism, Christianity, and Islam, and the homes of peoples of different nationalities and ethnicities. These routes increased the interconnectedness of countries in the Eurasian continent, facilitated exchanges and mutual learning between Eastern and Western civilizations, promoted regional development and prosperity, and shaped the Silk Road spirit characterized by peace, cooperation, openness, inclusiveness, mutual learning, and mutual benefit. The millennia-old Silk Roads symbolize communication and cooperation between East and West, demonstrating that by upholding solidarity and mutual trust, equality and mutual benefit, inclusiveness and mutual learning, and win-win cooperation, countries with different ethnic groups, beliefs, and cultural backgrounds can share peace and achieve development together. The Silk Road spirit aligns with the ideal of “all nations uniting in harmony and peace” that the Chinese nation has long upheld, with the Chinese people’s principles of friendliness and good neighborliness and “helping others succeed while striving for our own success,” and with the call of the era for peace, development, and win-win cooperation. It is essential to address these global problems such as slow economic growth, deficiencies in economic governance, and unbalanced economic development. It is no longer acceptable for a few countries to dominate global economic development, control economic rules, and enjoy the fruits of development. The Belt and Road Initiative targets development not only for China but for the entire world. Economic globalization remains an irreversible trend. It is inconceivable for countries to return to a state of isolation or seclusion. However, economic globalization must undergo adjustments in form and content. It must be more open, inclusive, balanced, and beneficial to all. China has not only benefited from economic globalization but has also contributed to it. As an active participant in economic globalization, China has achieved rapid economic growth through positive interactions with the rest of the world and has explored a unique path to modernization, expanding options for other developing countries to achieve modernization. China’s rapid economic growth and steady progress in reform and opening-up have provided strong impetus for global economic stability and growth, as well as an open world economy. China has been a strong advocate and defender of economic globalization. The Belt and Road Initiative aligns with the UN 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development in concept, measures, and goals. The Belt and Road Initiative, a major step taken by China, aims to promote high-quality development through higher-standard openness and share China’s development opportunities with the rest of the world. The Belt and Road Initiative is also a Chinese solution to global development problems, aiming to drive modernization in participating countries in parallel, making economic globalization more dynamic, inclusive, and sustainable, and ensuring that more fruits are shared more equitably among people worldwide. However, the growing deficits in peace, development, security, and governance, coupled with intertwined traditional and non-traditional security issues such as regional conflicts, arms races, food security, terrorism, cyberattacks, climate change, energy crises, major infectious diseases, and artificial intelligence problems, pose a serious threat to the beautiful planet on which all humans live. In the face of
Contract Manufacturing in China: Advantages and Disadvantages

For many years, China has been the world’s manufacturing center. Last year, production rates partially contracted due to the impact of COVID-19. This means China needs your business and there was no better time for manufacturing in the country. Key Advantages of Contract Manufacturing (OEM) in China:
Legal Challenges in Import and Export from China

China is a unique country, with a complex legal system that differs completely from the West. If you’re looking to do business in China, you’ll need to familiarize yourself with this unique legal landscape. Challenges of Starting Business in China: Choosing Business Structure: Reporting Responsibilities: Labor Laws:As in any country, you’ll need to comply with local labor laws regarding minimum wages, working hours, taxes, and more. Labor laws in China can differ significantly from Western countries, and are not always more lenient.
Luxury Goods Trade in China: Growing Market

Quick Overview: Challenges Across All Categories All luxury goods categories faced challenges, though their impact varied by category. The beauty sector – especially fragrances, color cosmetics, and ultra-premium skincare – showed stronger resilience as consumers seek emotional and sensory experiences. The fashion sector saw smaller declines compared to leather goods, largely due to its seasonal nature and the importance of the Very Important Customer (VIC) category. Overseas Shopping and Gray Market In 2024, there was a notable recovery in overseas shopping, especially in Japan, accompanied by significant growth in the gray market due to increased price differentials. Price differentials between luxury goods in mainland China and other markets, especially Japan, affected the mainland market and played a crucial role in reviving overseas luxury shopping. Future Outlook In 2024, China’s luxury goods market failed to maintain its previous growth trajectory, facing unexpected and severe slowdown that worsened throughout the year. The market is expected to continue its downward trend during the first half of 2025, with cautiously optimistic expectations appearing in the second half of the year. Key factors affecting the outlook include stronger government stimulus policies and the impact of the new US administration taking office in January.
